Fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly common due to today’s living habits. In this blog we will discuss what are symptoms of fatty liver disease, as well as potential causes, available treatments, and lifestyle modifications that can help avoid it. This blog will give you helpful information
What is Fatty liver Disease ?
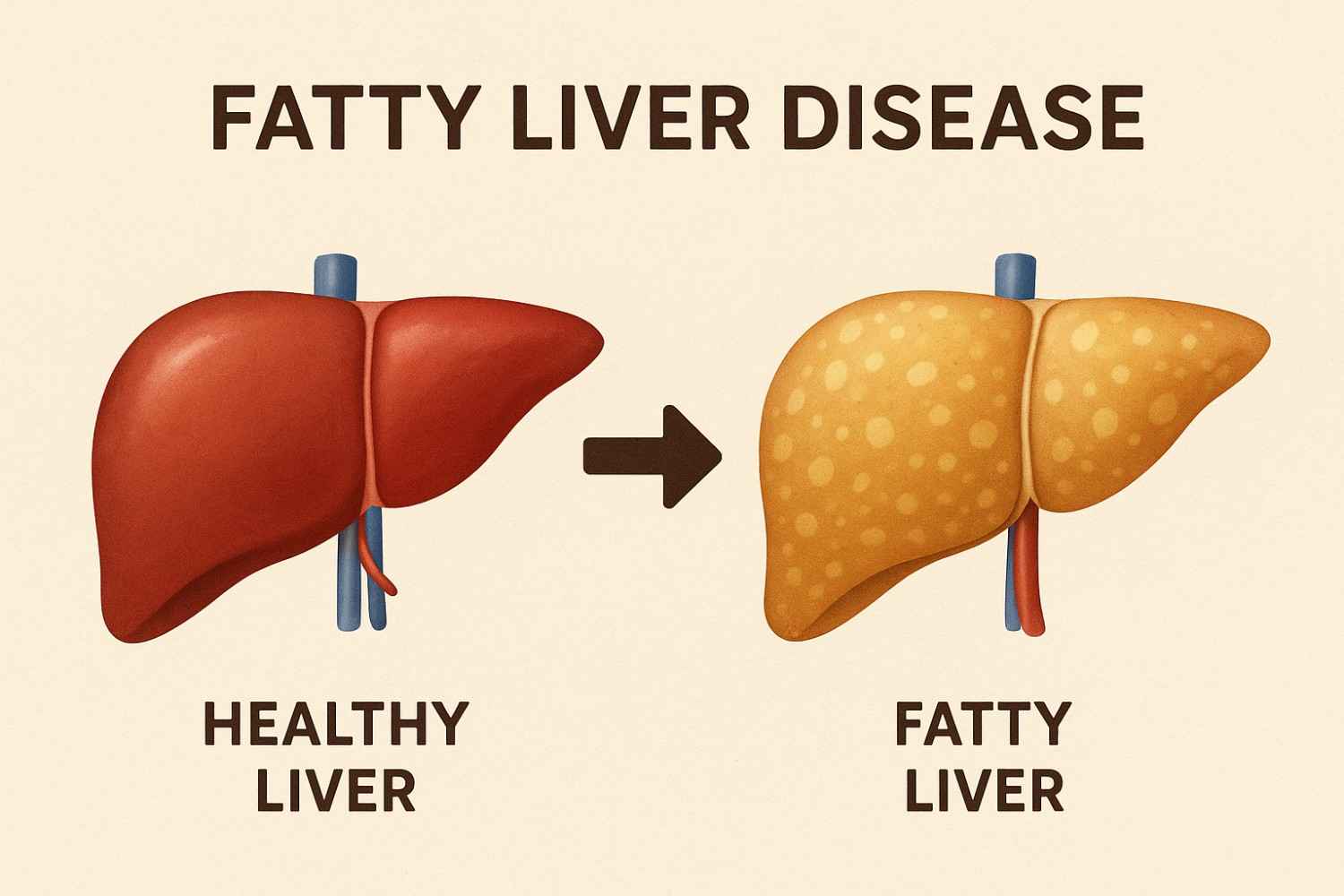
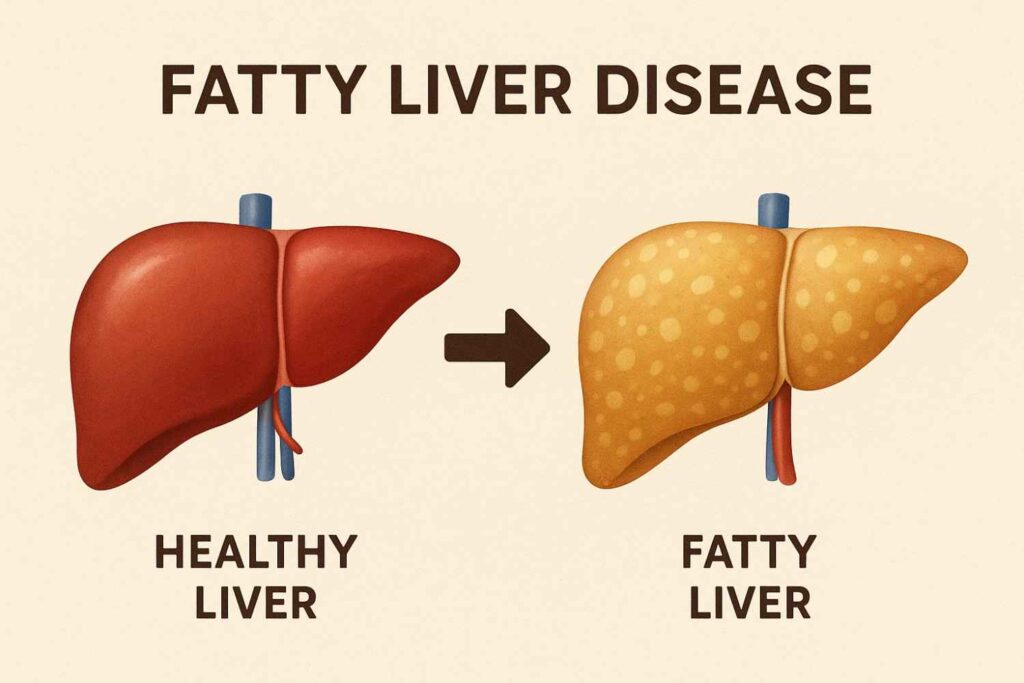
fatty liver disease, a condition in which the liver accumulates too much fat, can cause inflammation and damage to the liver. There are two primary sorts of it.:
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver dsease
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease
What is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease ?

A specific kind of fatty liver disease that is unrelated to excessive alcohol consumption is NAFLD. There are two types exist:
- Simple fatty liver is characterized by the presence of fat in the liver but little to no inflammation or damage to the liver cells. Usually, simple fatty liver does not get worse to the point of liver injury or problems.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by liver fat, inflammation, and damage to the liver cells. Fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver can be caused on by inflammation and injury to the liver cells. Cancer of the liver or cirrhosis can result from NASH.
What is alcoholic fatty liver disease ?
The cause of alcoholic fatty liver disease is excessive alcohol consumption. The majority of alcohol is broken down by your liver and eliminated from your body. But when it breaks down, toxic chemicals may be produced. These drugs have the potential to weaken your body’s defenses, cause inflammation, and harm liver cells. Your liver will suffer more harm the more alcohol you consume. The first stage of liver disease caused by alcohol is called alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis are the next stages.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease
t’s not necessarily signs of fatty liver disease.. When present, the following symptoms are present:
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right section of your abdomen (belly).
- Excessive weakness or tiredness (fatigue).
Symptoms are more frequently observed after SLD has advanced to liver cirrhosis. When you have cirrhosis, you might have:
- Nausea.
- Reduced appetite.
- Unnoticed weight loss.
- Jaundice, or yellowish skin and eye whites.
- Ascites, or abdominal swelling
- Swelling (edema) in your hands, feet, or legs.
- Bleeding (that your doctor discovers in your stomach, rectum, or esophagus).
Causes of Fatty liver disease
There are several causes of fatty liver disease. However, if you have a cardiometabolic risk factor, drink too much alcohol, or both, you have a higher chance of developing fatty liver disease .
The possibility of acquiring fatty liver disease is higher if you:
- Include an alcohol consumption problem (heavy or frequent alcohol use).
- Have the metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high triglyceride levels, and insulin resistance.
- Having type 2 diabetes .
- Hold a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2.
- have a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher, indicating obesity.Have PCOS, or polycystic ovarian syndrome.
- Have sleep apnea that is obstructive.
- Suffer from low thyroid levels, or hypothyroidism.
- Have low pituitary gland hormones, or hypopituitarism.
- Have low sex hormones, or hypogonadism.
What caused to the renaming of fatty liver disease as steatotic liver disease?
Steatotic liver disease was formerly referred to as “fatty liver disease.” To better reflect its causes, doctors renamed the illness and its subtypes in 2023. For instance, there are a number of risk factors that are not connected to weight or body mass index (BMI), even if some disorders like obesity that are linked to your body’s fat composition can raise your chance of developing steatosis.
Additionally, language that can make people with SLD is avoided in the renaming.
Does fatty liver disease create a significant risk?
The majority of the time, the accumulation of fat doesn’t result in major issues or stop your liver from operating normally.
The illness can sometimes develop into liver disease. Usually, it moves forward in phases:
Hepatitis: Your liver becomes enlarged and inflammatory instead of fatty. Inflammation causes tissue damage. Steatohepatitis is the name given to this stage.
Fibrosis: Your liver becomes stiff as a result of inflammation, forming bands of scar tissue. Fibrosis is the term for this process.
Large amounts of scar tissue replace healthy tissue in cirrhosis. Your liver is cirrhosis at this stage. If left untreated, cirrhosis can result in potentially lethal diseases such liver cancer and liver failure. Cirrhosis affects about 90% of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a form of liver cancer.
How may fatty liver disease or steatotic liver disease, be confirmed?
In order to diagnose you, your healthcare provider might do:
- A medical history that includes inquiries regarding your ailments, alcohol consumption, and medications.
- A physical examination to look for indications of cirrhosis, such as jaundice, or inflammation, such as an enlarged liver.
- Imaging tests, such as an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT scan (computed tomography scan), or ultrasound, to look for indications of scarring and inflammation in your liver. To find out how much fat and scar tissue is in your liver, they could prescribe a specialist ultrasound called FibroScan .
What is the treatment of fatty liver ?
There isn’t a particular drug or treatment. Rather, the providers concentrate on assisting you in controlling the risk variables which contribute to the problem. This includes changing your way of living in ways that will benefit your health.
- Avoid drinking: Avoid alcohol even if it has nothing to do with your SLD.
- Reduce weight: Medication, including GLP1RA, dietary changes (under a nutritionist’s supervision), and exercise can all aid with weight loss. You might be eligible for bariatric surgery, which can aid with weight loss.
- Manage metabolic problems with medication: Take recommended drugs to control blood fat (triglycerides), cholesterol, and diabetes. Vitamin E and thiazolidinediones (drugs used to treat diabetes, such as Actos and Avandia) may also be necessary in certain situations.
- Obtain the Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B vaccines: Those who currently have liver illness are particularly vulnerable to these viral infections .
Some lifestyle changes that can help with fatty liver disease
- Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing sugar and salt.
- Engage in regular exercise to help you lose weight and lower liver fat.
- Before taking any complementary or alternative medicine, medical procedures, or dietary supplements like vitamins, consult your physician. Your liver may be harmed by certain herbal medicines.
- Protect yourself from pneumococcal illness, the flu, and hepatitis A and B. Hepatitis A or B increases the risk of liver failure if it coexists with fatty liver. These two immunizations are also crucial since infections are more common in people with chronic liver disease.